Human history is a story of wars, moments of prosperity and… pandemics and epidemics.
Pandemics have mostly animal origins (zoonoses), while epidemics are caused by viruses and bacteria that are unknown to our immune system or that we have learnt to know and fight over time.
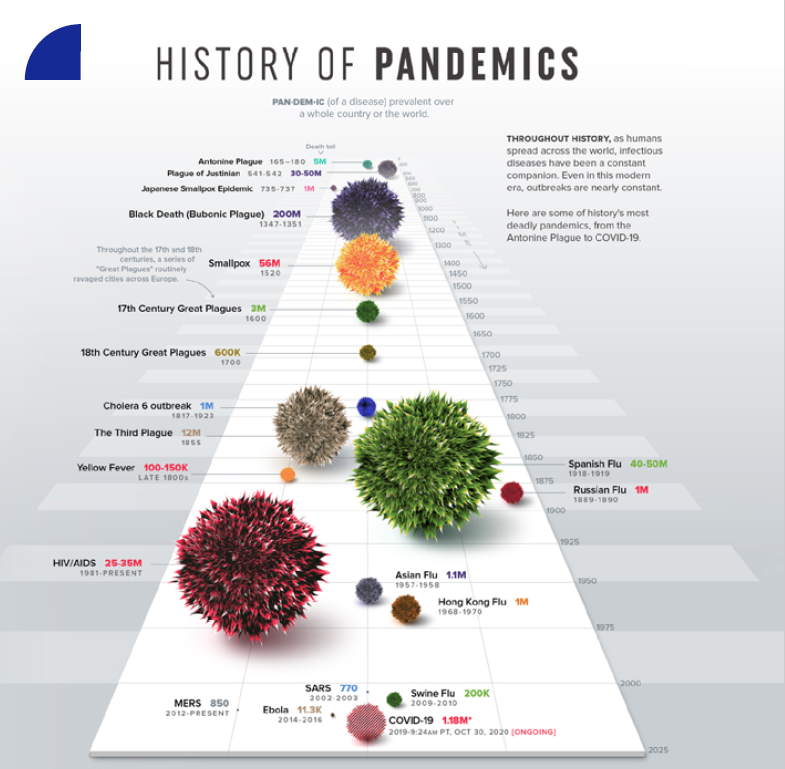
HISTORY OF PANDEMICS – credits: Comarch White Paper “Healthcare During and post COVID-19 Pandemic”
HIV is still considered by the WHO to be a full-fledged pandemic, having claimed over 33 million victims to date.
The last devastating pandemic was caused by the Spanish flu (1918-20), which is an example of how dangerous the collaboration between viruses and bacteria can be.
But as sanitation standards have spread and antiseptics have been developed, with free access to treatment for all, their frequency has fallen and, consequently, so has the mortality rate.
Epidemics and pandemics have also been discussed in more recent times. In 2009 with influenza A/H1N1 (also known as swine flu) and in recent months with Sars-CoV-2 (which caused the Covid-19 pandemic).
Pandemics and epidemics will be with us forever, as will the viruses and bacteria that cause them.
Discover the pandemic revolution and revelations
What is the difference in patient care and management between each of the different pandemics?
Covid-19 seriously threatened (and still is) the health of everyone, regardless of their geographical location. In the first months of 2020, it was declared a global pandemic by the WHO. Lockdowns and heavy shifts in hospitals became an endemic reality.
One of the biggest worries brought to light by the pandemic was the lack of preparedness. Hospitals were overwhelmed with patients, masks, gloves and disinfectants became unavailable for a short time. And it had been necessary to ask for support from other medical facilities (inside or outside the country).
However, most healthcare facilities have had to postpone or cancel long-planned procedures, and limit access to specialist care and diagnostic tests.
Health institutions, supported by media and social channels, conducted public awareness campaigns on both personal and and environmental hygiene. And everyone still wears individual protective devices such as facemasks, we carry sanitisers and we practice physical distancing.
But these were not the only changes. We have long talked about telemedicine, video consultations and electronic health records, but never before have start-ups and companies been able to make the most out of the digital tools available to improve the healthcare journey and patient care.
In a much shorter time than in the past, it was possible to carry out genomic sequencing of the virus and thus develop the vaccine.
Remote monitoring and new ways of communicating between doctors and patients
The practice management has been transformed by the Covid. Doctors, in order to minimise the spread of Sars-Cov-2 infection and limit face-to-face visits and unnecessary patient travel, have had to adopt digital tools and define new admission guidelines.
Since the digital innovation made its way into healthcare, its impact on the patient journey has been crucial.
Read more about virtual communication between doctor and patient
In fact, all the steps from information gathering to diagnosis, through consultations and treatment, have been simplified and made increasingly accessible thanks to the integration of digital tools such as smartphones, apps, video-visits, chatbots, etc. .
The digitalisation of the patient journey has certainly enabled doctors to create more flexible, personalised and facilitated ecosystems of care in order to connect with their patients and better organise their daily activities through telemedicine services such as video visits and remote monitoring at home. In addition, it enables the exploitation of automated systems for receiving and forwarding reports, prescriptions, etc.
A remote patient monitoring system usually comprises a telemedicine platform processing data from integrated and embedded sensors, as well as patient applications. Comarch HomeHealth is a perfect example of such a solution.
Some of the solutions which enable constant patient monitoring in the case of cardiovascular diseases include Comarch CardioNow and Comarch CardioVest. which can also send data to the Comarch e-Care platform. Thanks to artificial intelligence solutions, they detect and identify anomalies in a patient’s ECG, facilitating the diagnosis of arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation and other heart disorders.
There is also a need for software that guarantees safe and effective remote medical consultations.
In order to address the emerging need, Comarch MedCall software suite was developed. This is an intuitive tool designed for video consultations and teleconsultations, dedicated to medical institutions, group and individual medical practices, which offers secure audio and video communications with patients via a mobile application.
Local health care beyond medical facilities
With the spread of the Covid-19 pandemic, the health sector has undergone a significant acceleration towards digital.
The new requirements demand the need to remotely monitor the patients wherever they are and promptly take action if needed. While home monitoring can help fight the spread of the virus, the telemonitoring services ensure a continuum of care for patients with suspected or confirmed Covid-19 infection.
Digital solutions such as remote telemonitoring have made it possible, and continue to make it so, for GPs to monitor the vital parameters of their patients with suspected or confirmed Covid-19 infection, in home isolation and with low to medium severity conditions.
Products such as Comarch Diagnostic Point play the role of self-service health checkpoints, as they can be installed in offices, airports, gas stations and shopping malls.



