Enhancing Patient Outcomes and Surgical Care
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly revolutionizing the field of healthcare, but its integration in surgery has been relatively nascent. However, a recent study published in Nature1 explores the potential of AI in surgery, highlighting its multifaceted improvements in preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care.
Artificial Intelligence in surgery: the study
The study emphasizes the significant global burden of surgical procedures, with over 330 million performed annually. It also highlights the existing challenges in terms of access to surgery, postoperative complications, and mortality rates. With the potential to address these issues, AI offers a promising way forward.
Traditionally, minimally invasive surgery has been at the forefront of improving surgical outcomes. However, the study points out that data-driven methods, empowered by AI, will play an increasingly important role in advancing surgical care and patient outcomes.
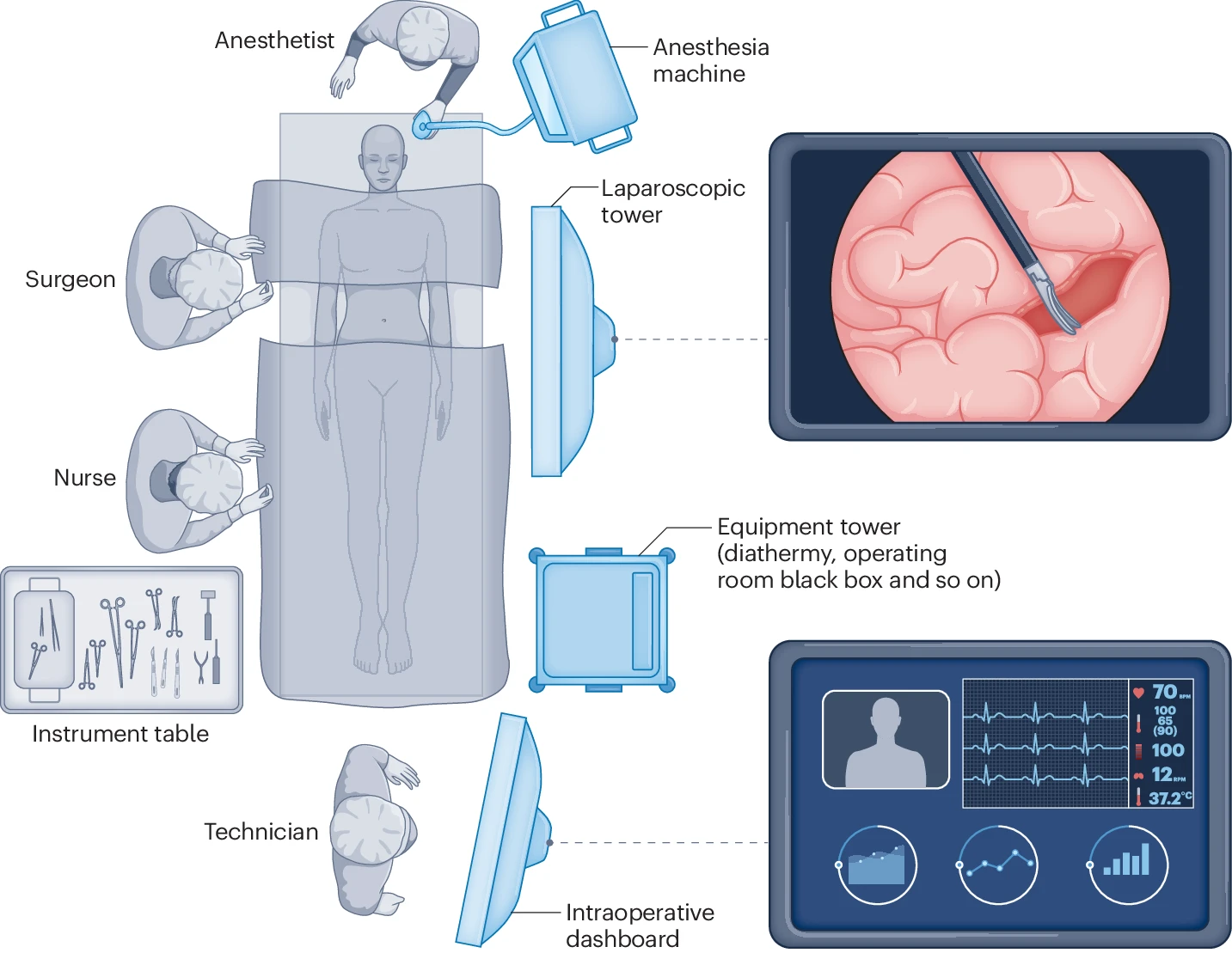
Integration of novel AI-powered digital interventions in the intraoperative setting
AI applications in surgery currently mostly rely on unimodal deep learning techniques. But transformer models, a recent breakthrough in neural network architectures, show great promise in enabling multimodal AI and foundation models. These models have the potential to handle diverse data formats and optimize surgical care across all stages of the process.
The integration of AI in surgery encompasses a wide range of applications. These include clinical risk prediction, automation and computer vision in robotic surgery, intraoperative diagnostics, enhanced surgical training, postoperative monitoring through advanced sensors, resource management, and discharge planning, among others.
The study envisions AI as a key tool to improve various aspects of surgical care. Preoperatively, AI can aid in patient selection, diagnostics, and surgical planning. For example, reinforcement learning algorithms have shown promise in identifying and maximizing tumor tissue removal while minimizing damage to functional anatomical tissues during neurosurgery. Virtual reality combined with AI-based segmentation systems can also enhance preoperative planning by aiding in complex surgical cases.
AI and preoperative diagnosis: the outcomes
Accurate preoperative diagnosis is crucial in surgical practice, and AI can significantly contribute to this area. The study highlights the successful application of AI algorithms in extracting unstructured radiological report data to enhance breast cancer diagnostics. Additionally, three-dimensional convolutional neural networks have demonstrated high accuracy in detecting pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas, enabling early intervention and treatment.
AI plays a pivotal role in clinical risk prediction as well. By accurately assessing patient risks, it can facilitate enhanced patient selection, informed consent, and shared decision-making. However, the study also emphasizes the need for further research to mitigate biases and improve the overall accuracy of clinical risk scores.
By integrating AI into surgical care, healthcare professionals can optimize surgical workflows, reduce complications, and improve postoperative monitoring. The study concludes with a call for the development of novel transformer models capable of integrating and analyzing vast amounts of data, paving the way for even greater advancements in surgical AI in the near future.
In conclusion, the study published in Nature highlights the immense potential of AI for enhancing patient outcomes and surgical care. With its applications in diagnosis, risk prediction, and surgical planning, AI is poised to revolutionize the field of surgery. As technology continues to advance, the integration of AI promises a new era of surgical innovation and improved patient care.
1 Varghese, C., Harrison, E.M., O’Grady, G. et al. Artificial intelligence in surgery. Nat Med (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-02970-3



